Complete DMA Workflow
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Overview
Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a high-level cheating method used in video games that is particularly difficult to detect. This guide explains what DMA is, how it works, and requirements for using it.What is DMA?
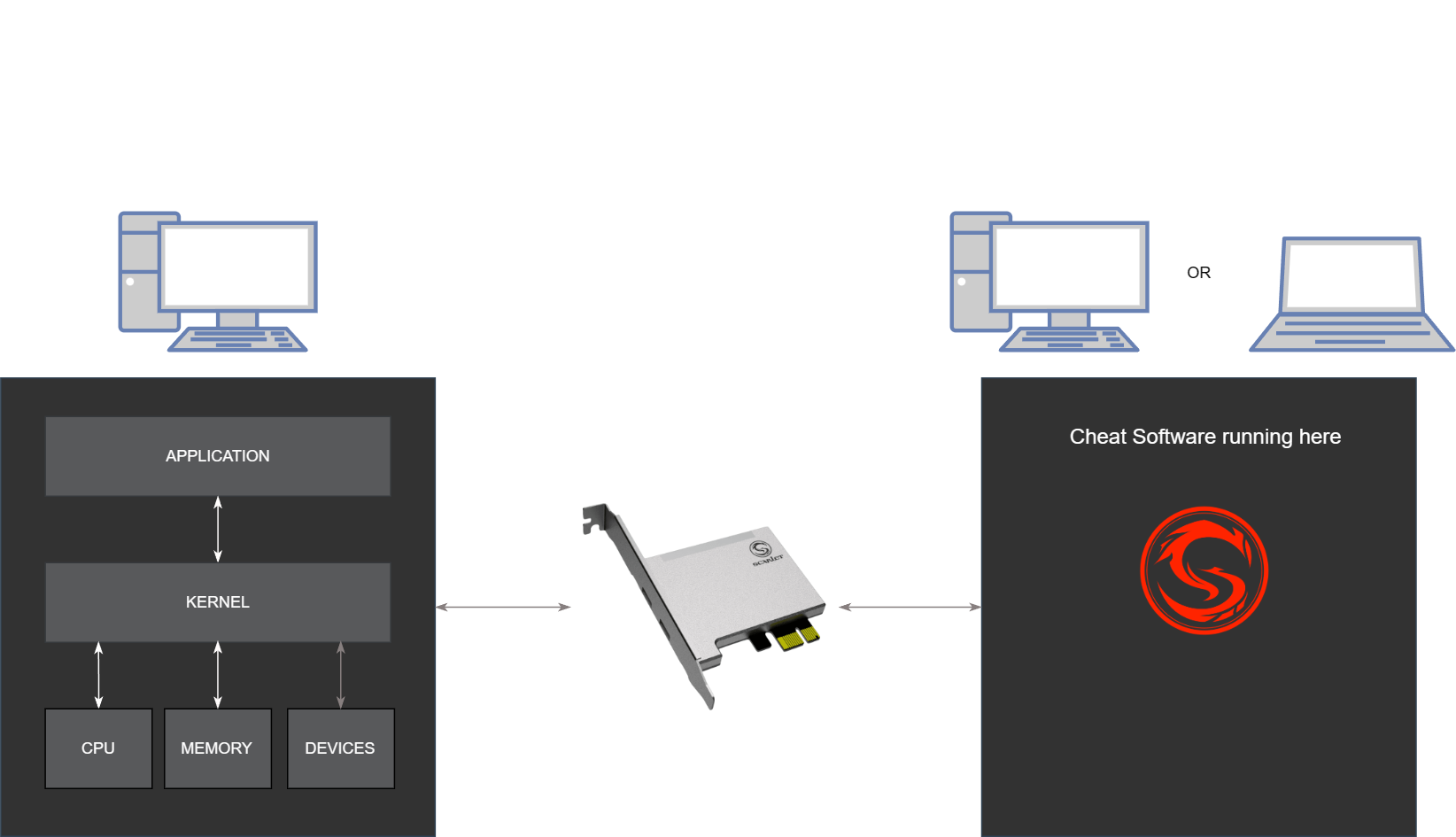
DMA is a feature that allows hardware to access system memory directly, bypassing the CPU. Since DMA operates at the hardware level outside normal OS operations, it can manipulate game data without detection by traditional anti-cheat systems that monitor software behavior.How it Works
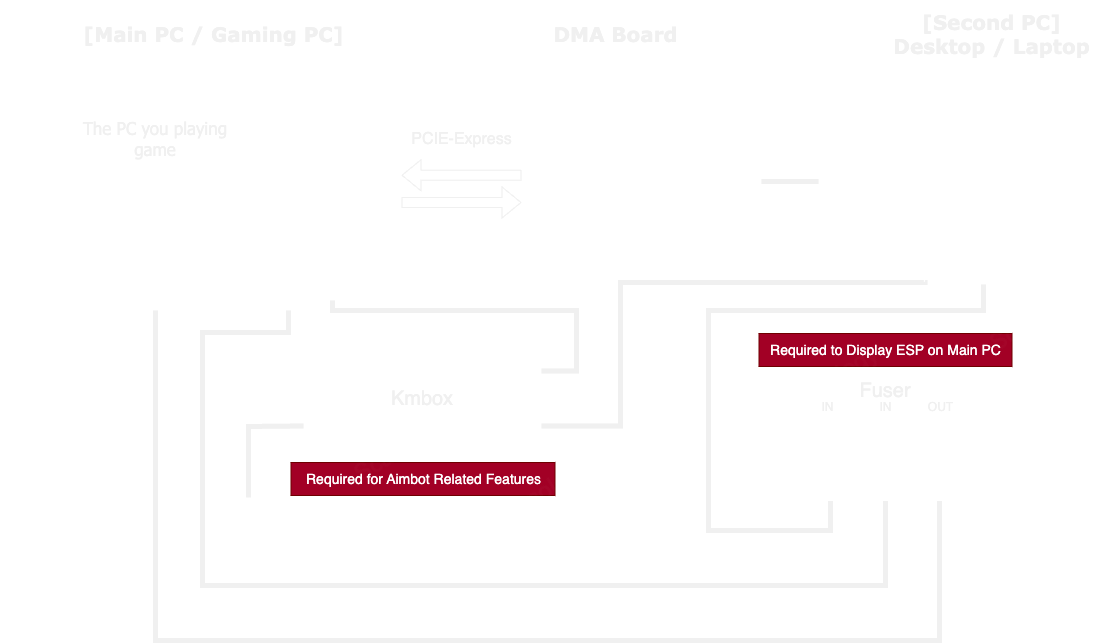
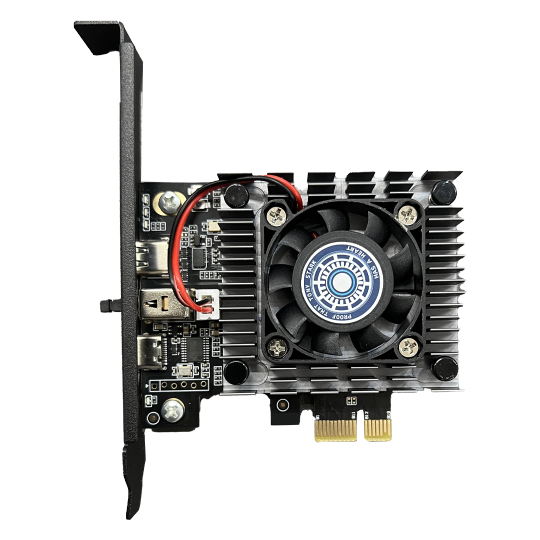
DMA uses a small board (approximately palm-sized) that fits into a PCIe slot, similar to a graphics card slot. This board connects via data cable to a second computer.Credit: Ufrisk - Original Creator of PciLeech

System Requirements
Checking DMA Compatibility
To determine if your motherboard supports DMA:- Press
WIN+Rand typemsinfo32.exe - Look for “Kernel DMA Protection” in the system information
- If it shows OFF, your motherboard supports DMA

Primary Computer Requirements
DMA requires two computers to function. For the Gaming PC:Desktop Requirements
- Available PCIe slot (x16, x4, or x1)
- PCIe extender if slots are blocked by GPU
- Sufficient performance to run games smoothly
Laptop Requirements (Not Recommended)
Must have one of:- Extra M.2 slot (for M.2 to PCIe converter)
- Extra M.2 slot (for M.2 version DMA)
- Thunderbolt 3 port (for Thunderbolt to PCIe converter)
External PSU may be needed to power DMA when using M.2 conversion
Second Computer Requirements
The second computer can be either desktop or laptop with: Minimum Specs:- CPU: Intel i5 4th gen or better
- GPU: Integrated or Dedicated Graphic Card
- CPU: Intel i5 9th gen / Ryzen 5600G or better
- GPU: Integrated or Dedicated Graphic Card (Minimum support must be the same resolution as a Gaming PC)
